Atopic Dermatitis
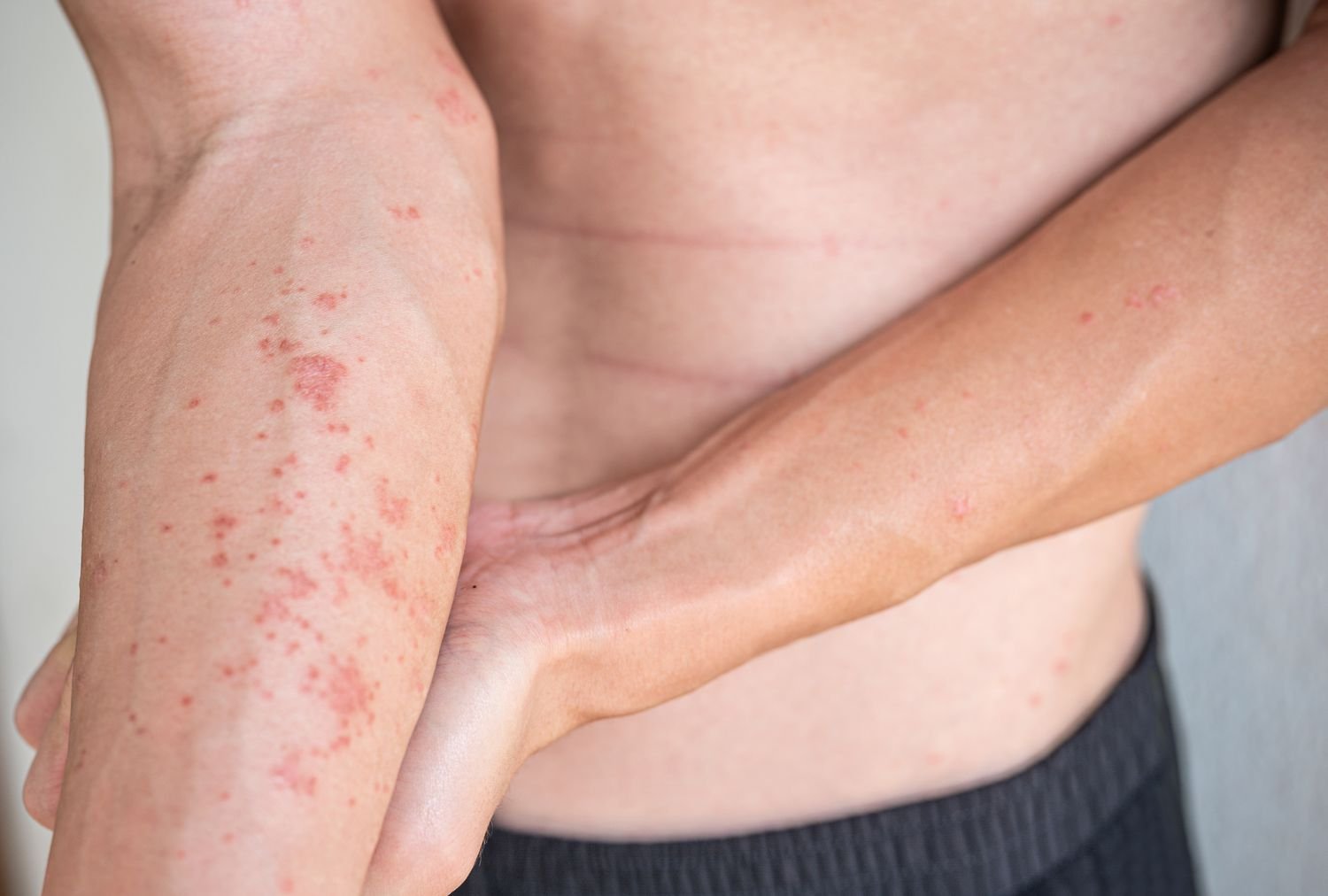
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, can affect people of all age groups, including adults. The symptoms of atopic dermatitis in adults are similar to the condition in children. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Adults may experience red or brownish-gray patches of skin, intense itching, dry and scaly skin, small, raised bumps that may leak fluid if scratched and thickened or cracked skin.
It can be triggered or exacerbated by several factors. These can include dry skin, irritants (such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics), allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander), certain foods, stress, heat or sweat, and hormonal changes.
Atopic dermatitis can significantly impact quality of life as itchiness and discomfort can interfere with sleep, work, and daily activities. The visible skin symptoms may also cause self-consciousness and emotional distress.
Treatment options for atopic dermatitis can include:
- Moisturizers: Consistently application of moisturizers or emollients to keep the skin hydrated.
- Topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators: These medications can help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines may be prescribed to help relieve itching and improve sleep.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that worsen symptoms.
- Wet wrap therapy: Applying wet dressings to affected areas to soothe and hydrate the skin.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Managing atopic dermatitis in adults may also involve making certain lifestyle adjustments, such as:
- Using gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents.
- Avoiding scratching or rubbing the affected skin.
- Wearing soft, breathable fabrics.
- Managing stress levels.
- Taking steps to maintain a healthy, balanced diet.
- Avoiding excessive heat or excessive sweating.
- Biologics treatment for severe and persistent cases.
Biologics are a class of medications that target specific molecules in the immune system. They are used to treat various conditions, including atopic dermatitis by reducing inflammation and controlling the symptoms of atopic dermatitis. They are highly effective and are approved for treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. These include dupilumab, which targets IL-4 and IL-13, and tralokinumab, which targets IL-13.
Biologics have shown promising results in clinical trials for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. They have been found to significantly improve skin symptoms, reduce itchiness, and enhance quality of life in patients with moderate to severe disease who have not responded well to other treatments.
They are typically administered through subcutaneous injections. The frequency of injections can vary depending on the specific medication prescribed, ranging from once every two weeks to once every four weeks. Like any medication, biologics can have side effects. Common side effects may include injection site reactions, conjunctivitis (pink eye), and upper respiratory tract infections. However, serious side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions or an increased risk of certain infections. It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of biologics with your healthcare provider.
Consultation with healthcare professionals:
If you are experiencing symptoms of atopic dermatitis, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide you with an accurate diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and offer guidance on managing the condition effectively.



